Dependency insurance, a new niche for insurers
Nursing services provided by close relatives or by professionals has become necessary in order to continue living a normal life. Moreover, any accident resulting in prolonged loss of autonomy may require huge costs. This kind of assistance incurs costs that may quickly outweigh the available resources .
However, the services and fees pertaining to nursing are not covered by social security institutions. To offset this shortcoming, insurers have designed a scheme, called dependency insurance or autonomy loss plan.
Dependency insurance: a new class of business
 Fotolia‘s standard licence Fotolia‘s standard licence |
Dependency insurance shall provide coverage for the costs sustained by some individuals in order to carry out the tasks of daily life. Recourse to insurance makes it possible for these individuals not to squander the capital available and not become a burden for their family.
Dependency insurance is relatively a new concept that has been imposed by the new life styles.
The role of the State
For ages, it has been widely believed that coverage of the cost pertaining to the assistance for the elderly is a private matter that the State has nothing to do with. While developed countries have managed to come up with solutions to this issue by providing an inclusive comprehensive health insurance scheme, State initiatives remain quite limited.
Insurers have come to realize that the coverage deficit at the level of public authorities has opened windows of opportunities, enabling them to design specific products. The real issue affects countries suffering from aging populations.
With declining fertility, the improvement of life expectancy, tightening public social security, underwriting a private dependency insurance policy has become more of a necessity.
Definition of dependency insurance

Loss of autonomy may be the consequence of an accident, a handicap, a disease, or old age. To offset this happening, the insured will resort to underwriting a policy that enables them to benefit from a capital or from an annuity covering the services related to the loss of their autonomy.
This insurance scheme may be obtained by means of a pension plan or a life insurance contract. For the former, dependency insurance is the main guarantee of the policy whereas in the second, it is a complementary plan.
Loss of independence insurance is therefore a guarantee with deferred lump sum, financing the services provided to the underwriter in the event of total or partial dependency noted.
The use of dependency insurance
Dependency insurance has been designed to meet a series of needs:
- It preserves the assets saved during active life,
- It keeps the insured from being brutally confronted with a desperate situation,
- It enables the policyholder not to be a burden for his relatives,
- It spares young generations the issue of forfeiting the bulk of their revenues to support their parents. Some legislation has introduced a compulsory provision whereby children are required to take care of their parents. This kind of assistance may be tantamount to placing their parents in nursing homes.
Loss of independence insurance is related to population, societal and the economic changes. These factors are behind its current development. In countries endowed with mature economy, this class of business is getting more and more important.
Population changes
Developing countries have experienced an improvement in the life expectancy of their population ranging from 30% to 75% in the last 55 years. The gap with developed countries has been reduced over the same period:
Variation of life expectancy in some Asian countries
| Life expectancy | Evolution of life expectancy over the last 55 years | Variation of life expectancy compared to the United States | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1950-1955 | 2005-2010 | 2050-2055 | 1950-1955 | 2005-2010 | 2050-2055 | ||
China | 44.6 | 72.7 | 79.7 | 63% | -24 | -5.3 | -3.8 |
Hong Kong | 63.2 | 81.66 | 87.7 | 29% | -5.5 | 3.6 | 4.1 |
India | 37.9 | 64.2 | 74.4 | 69% | -30.7 | -13.8 | -9.1 |
Indonesia | 38.8 | 67.9 | 78.2 | 75% | -29.8 | -10.1 | -5.3 |
Japan | 62.2 | 82.7 | 87.9 | 33% | -6.5 | 4.8 | 4.3 |
South Korea | 47.9 | 80.6 | 85.1 | 67% | -20.7 | 2 | 1.5 |
Malaysia | 55.4 | 73.4 | 80.3 | 32% | -13.2 | -4.6 | -3.3 |
Philippines | 55.4 | 67.8 | 77.1 | 22% | -13.2 | -10.2 | -6.5 |
Singapore | 60.2 | 80.6 | 85.7 | 34% | -8.4 | 2.6 | 2.1 |
Thailand | 50.7 | 73.6 | 80.1 | 45% | -17.9 | -4.4 | -3.5 |
Source: “Long-term Care at a crossroads: delivery of adequate protection to the wider public”, Dirk Nieder and Alex Leung
Global population is ageing throughout the years, a phenomenon that is steadily gathering momentum. Life expectancy has also been rising in developed countries even though this ageing is taking place less quickly in emerging countries.
Population aged over 65 expressed in percentage of the total population: 1960-2050
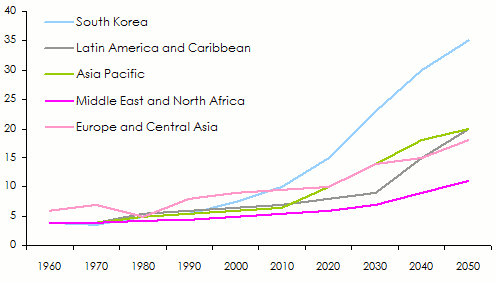 Source: The World Bank. Population estimates and projections. Health, Nutrition and Population Statistics 2013
Source: The World Bank. Population estimates and projections. Health, Nutrition and Population Statistics 2013
 Fotolia‘s standard licence Fotolia‘s standard licence |
Regarding fertility, the number of children per woman has declined significantly. This decrease which started in developed countries, is now detrimentally affecting developing countries.
In Asia, for instance, fertility has dwindled down from 60% to 80% over the last 55 years. In China, it has been decreasing by 73%, in Hong Kong by 78%, In Singapore by 81%, in South Korea by 75% and in Thailand by 73%.
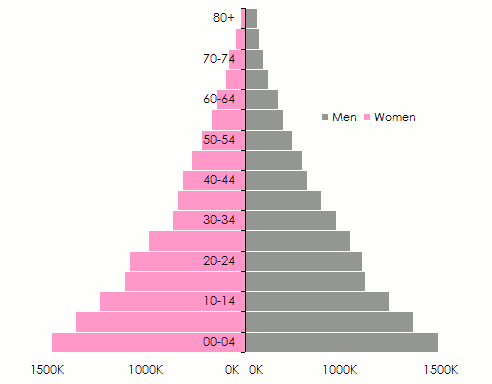
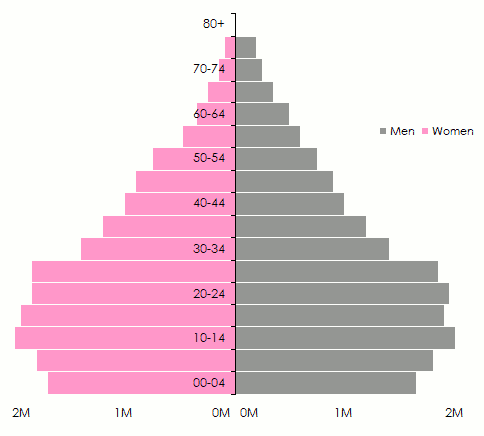
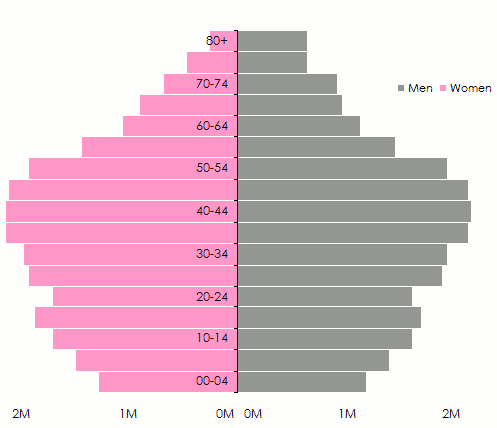
Age pyramids are globally switching from the pyramidal pattern, characterizing countries with young population, toward a pattern whereby oldest population will be more numerous.
Evolution of the population pyramid for developing countries
1960
1990
2010
2030
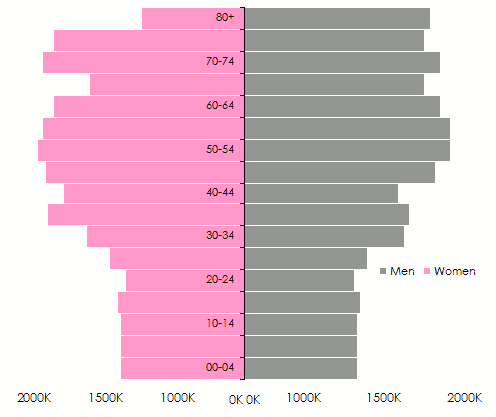 Source: The World Bank. Population estimates and projections. Health, Nutrition and Population Statistics 2013
Source: The World Bank. Population estimates and projections. Health, Nutrition and Population Statistics 2013
Societal changes
Modern societies have sustained numerous shocks and upheavals in the recent 50 years. Falling marriage numbers, rising divorce numbers and the reduction in family size stand as the most notable changes.
Evolution of the number of marriages in the emerging countries of Asia, in Germany and in the United States
(Annual number of marriage per 1000 population in age range 20-49)
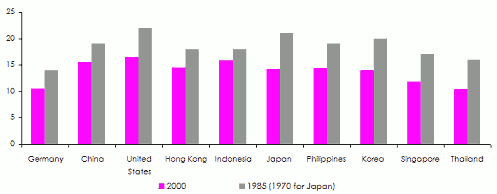 Source: The World Bank. Population estimates and projections. Health, Nutrition and Population Statistics 2013
Source: The World Bank. Population estimates and projections. Health, Nutrition and Population Statistics 2013
Another phenomenon witnessed in emerging countries: the average age of the first marriage has gone down whereas divorce rate has sometimes gone twofold in ten years’ time. As a consequence, the average family size has declined, getting closer to that of developed countries.
The increase in the number of working women has adversely affected birth rate figures.
Eventually, as children are getting less and less keen on living with their parents, the phenomenon of elderly dependency has grown bigger.
Economic changes
The costs pertaining to social security systems stand as a particularly important charge borne by modern States.
In an economic context dominated by unemployment, governments are required to make choices, as they are no longer able to put up with all of the expenses earmarked for an ageing population.
ublic benefits are struggling ever more to be insured. Consequently, citizens are turning to private insurers in order to finance their needs in the event of dependency. The issue regarding the compulsory plan for loss of autonomy is already on the agenda in some countries.
The functioning of loss of dependency insurance
The total or partial cover of loss of independence can come into effect as of the first day when the insured becomes unable to perform some basic activities in daily life: feeding oneself, getting dressed, moving, showering etc. this loss of independence may be triggered by a physical or mental state.
A partially dependent insured is the one who is no longer able to perform a certain number of limited acts. When this same insured becomes unable to perform numerous acts of daily life without assistance, he or she is then considered to be in a state of total dependency. According to the guarantees provided for by the contract, the insurer shall disburse to the benefit of the insured a life long annuity and/or a fixed capital and/or provide home nursing services.
In some cases, the insured may join both annuity and capital, the latter being made available for the insured during the first settlement. This scheme has been designed, among others, to accommodate or equip the home of the insured so as to facilitate its use and annihilate the effects of impairment.
The extent of disability is to be set after a medical evaluation. Once the rate has been established, it is applied to a compensation grid or scheme integrated in the insurance contract. Determining the rate of dependency shall be carried out by the medical expert only after impairment consolidation.
Dependency cost
The costs incurred by partial dependency case are lower than those sustained by total dependency. However, from a statistical point of view, the risk of partial dependency is higher than that of total dependency. Furthermore, this first risk requires a longer period than the total dependency risk. Ultimately, the partial dependency plan is, therefore, more onerous than that pertaining to total dependency.
The medical questionnaire
The dependency guarantee is not provided by the insurer unless the case of the applicant customer has been previously examined. It is based on the insurance proposal and the medical questionnaire filled out by the proposed insured that the risk will be assessed in terms of its insurability, the guarantees proposed, and the price of the guarantees. For individuals presenting aggravated risks, the insurer may require additional medical check-ups. The insurer reserves the right not to grant coverage to the proposed insured.
The waiting period
Some insurance contracts authorize risk management only after a period of time that may extend over three years following the signing of the contract. During this period, the coverage is suspended even if dependency has been established.
The waiting period does not apply if risk materialization is caused by abrupt accident.
Claims waiting period
 Some insurance contracts may impose a grace period on the insured. In this case, the insurer will cover dependency fees only after a period generally set in months. The insured’s first disbursements take place three months after the establishment of the state of dependency.
Some insurance contracts may impose a grace period on the insured. In this case, the insurer will cover dependency fees only after a period generally set in months. The insured’s first disbursements take place three months after the establishment of the state of dependency.
The grace period may come as a supplement to the waiting period.
The rates of loss of independence insurance
The premium paid by the insured depends on:
- Age: the higher the age of the contracting party, the more expensive the rates are. The rate grows according to age that triggers a deterioration of the health. An advanced underwriting age also means a shorter period of contribution,
- The health status of the underwriter as established by the medical questionnaire,
- The amount of the annuity or the capital underwritten,
- The scope of the guarantees offered by the insurance contract.
Premium settlement
Three payment modes are generally proposed to the insured:
- The single premium: It is high as it stands for the amount of capital underwritten.
- The split premiums: they may be settled during a period that may extend over 20 to 25 years but stop being settled as soon as the risk is established. The benefits are therefore provided to the insured who benefits from the guarantees as stipulated when policy was taken out. In the event the insured stops paying the premiums before the occurrence of the loss of independence, the annuity due by the insurer is therefore proportional to the period of premium settlement. A penalty may also be levied.
- Life-long premium: Unlike split premium disbursed to the insurer for a period of time, the life-long premium is due by the insured until his/her death or until the occurrence of loss of independence. As is the case for split premium, when the risk materializes while the contributions are no longer paid, the annuity allocated by the insurer is proportional to the period of premium payment. The contract may also provide for a heavy penalty to be levied against the insured.
Loss of independence insurance is generally qualified as a sunk insurance. Should the risk fail to materialize, the premiums remain property of the insurer.
Home benefits proposed by the dependency insurance
 Home benefits are often partially covered by social security institutions. Nonetheless, some insurance contracts may provide for entitlements to home services, either as a supplement to those provided by social bodies or comprehensively borne by the insurer.
Home benefits are often partially covered by social security institutions. Nonetheless, some insurance contracts may provide for entitlements to home services, either as a supplement to those provided by social bodies or comprehensively borne by the insurer.
These services are highly appreciated by retired people. The guarantees provided are designed to offset the difficulties encountered by the insured following prolonged work stoppage or an accident. Additional services may be accomplished by members of the family, or by professionals. Generally, it is (non-exhaustive list):
- Assistance to get fed or to cook
- Meal delivery
- Assistance for bodily wash
- Household assistance including laundry
- Assistance for mobility including shopping
- Adapted assistance for wheelchairs or special beds
- Day or night care
- House refurbishment: transformation of showers for easier access, adapting of doorways etc
- Hairdressing at home
- Pet care
- Transfer to hospital
- Medicine delivery
- Memory training drills
Public aid
In some countries, some support is provided to dependent individuals in the form of public allocations often financed by tax revenues or specific taxes. For instance, the introduction in France in 1956 of a vehicle traffic tax(1)designed to finance aid to elderly people.
The different kinds of dependency insurance contracts
A dependency insurance contract may be underwritten individually or within the framework of a collective contract initiated by a corporate entity, generally a company for the benefit of its employees.
Insurers have drawn up two major kinds of dependency coverage: Pension contracts and saving contracts (life insurance).
Pension contracts
Pension contracts are often underwritten during the fifties and may be pursued up to the age of 75 or even 77. A medical questionnaire is submitted to each insured. The amount of the contributions depends on the age of the insurance taker when taking out the policy.
During the materialization of the risk, that is, upon declaration of the state of dependency, the insurer is required to proceed with the payment of benefits as per contract.
On the ground, most pension contract play out only in the event of total loss of independence of the insured.
Savings contracts
Some life insurance contracts may also provide coverage for loss of independence. Consequently, should the dependency risk materialize, the saved-up capital shall be distributed to the insured in the form of annuity, an onerous solution, targeting well-off customers in the first place.
Additional guarantees
Most of dependency contracts provide the insured with additional covers such as assistance at home and various services. Such services are provided in return for the payment of a surcharge that may turn out to be quite high.
(1)Tax removed in 2000 for private cars
