Insurance captives
Insurance captives: Definition
A captive is an insurance or reinsurance company belonging to a company or to a group that does not operate in the insurance field, and whose task is to provide policies for parent company and for the group firms.
What are the types of insurance captives?
Direct insurance Captives assume the same function as a direct insurer. They are quite scarce due to the strong regulations binding the insurance sector.
Reinsurance Captivesare more frequent. They act as the reinsurer of the direct insurer and may themselves retrocede part of the assumed risks.
The rent-a-captives are captive accounts rented from reinsurers. Such a type does not require capitalisation from the start.
Insurance captives: What type of risks do they cover?
- The risks traditionally ceded to the insurance market.
- Non-insurable risks such as:
- New technology-related risks.
- Asbestos or pollution-related risks.
- Risks pertaining to concurrent dangers such as prolonged post office or transport strikes.
- Risks of commercial nature such as exchange risks, political risks, or raw material rate fluctuations.
- The risks that are not incumbent on the group but on the clients. In this case, the Captive acts as a traditional insurer.
| Advantages of insurance captives | Drawbacks of insurance captives |
|---|---|
|
|
Why this new interest in insurance captives?
The abrupt turnaround of the insurance market following September 11thattacks and the financial crisis that ensued is characterized by:
- an important reduction in the potentiality of both insurers and reinsurers,
- the necessity to cover certain risks (terrorism, natural disasters) requiring the payment of obligatory extra premiums,
- the considerable increase of basic premium and excess levels.
Such a situation made many companies aware of the high costs of insurance, and for some these charges are merely unbearable and certain risks will have to remain uncovered, hence, the necessity for these firms to think about transfer solutions through alternative structures such as self-insurance, pools, risk-retention groups as well as Captives.
Insurance captives throughout the world
According to “Best Captive Directory 2001”, 4 458 active Captives are listed all over the world, 30% of which are established in Bermuda. The other main locations are the Cayman Islands followed by the state of Vermont in the United States.
Distribution of insurance captives in the world
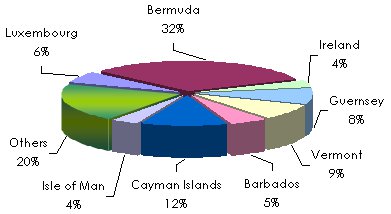 Source : Best's Captive Directory 2001
Source : Best's Captive Directory 2001Insurance captives in Emerging Countries
The evolution of insurance captives throughout the world has been accompanied by an equally-important evolution in Africa, namely in austral African countries where cellular Captives similar to rent-a-captives started to develop since 1993. However, this evolution took place in the absence of specific legislation.
Endeavouring to provide a more appealing framework to private underwriters, certain emerging countries have regulated the sector. Two countries committed to this principle are Bahrain and Mauritius.
Insurance captives in Bahrain
In its effort to consolidate the monetary market occupied by Bahrain during recent years, the Bahrain Monetary Agency, (BMA), has published on April 8, 2003, the new regulations governing the creation of Captives in Bahrain.
This official document entitled “Building a new insurance regulatory framework” sets the legislation, the field of activity and establishment procedures.
Insurance captives in Mauritius
It was in 1998 that the government of Mauritius proceeded to the legislation of the first regulations. These measures had an immediate effect on the Captives set up in the Mauritius, doubling their number.
Captive insurances activities are governed by the legislations in the “Financial Services Development Regulations 2001”.
