The cyber insurance market
 According to Moody's, cyber insurance is a relatively new segment of property and casualty insurance. The terms and conditions of cyber policies have not yet been standardized by the various market players.
According to Moody's, cyber insurance is a relatively new segment of property and casualty insurance. The terms and conditions of cyber policies have not yet been standardized by the various market players.
For the time being, this subcategory of property and casualty insurance is characterized by the absence of statistical data, the systemic nature of the risk and the danger of accumulating claims.
These particularities are compounding the misery of insurers who have difficulty quantifying their commitment and pricing the product. In addition, the systemic aspect of the risk leads to a problem of insurance and reinsurance capacity.
Cyberassurance, un marché en déséquilibre
Cyber risk insurance is far from being profitable for professionals as the market is facing a lack of capacity, caused by the imbalance between the premiums collected and the indemnities paid.
The readjustments made during the last renewals such as rate increases, coverage limits and stricter underwriting requirements, have resulted in a limitation of capacity, which hinders companies in need of solutions adapted to their needs.
Exclusion and reduction of coverage
While the cyber risk is at the heart of all the fears of the economic actors, some insurers do not hesitate to withdraw from this class of business. Other players continue to underwrite these risks but delimit their coverage more precisely or reduce it altogether. It is in this spirit, that Axa, Generali, AIG and The Lloyds have adopted more or less similar strategies for cyber insurance:
- Starting 1 January 2023, AXA will exclude cyber coverage from its liability policies. For the French group, the complexity of the risk no longer allows its integration into classic policies. It must be the subject of specific coverage with specific clauses, limits and pricing.
- Since the end of 2021, Generali has implemented a more restrictive cyber risk underwriting policy. For example, the Italian insurer no longer covers ransom payments made by companies that are victims of cyberattacks.
- The American giant AIG, on its part, has terminated 30% of its cyber policies, excluding the risk from its liability coverage.
- Lloyd's of London, on its part, is tightening exclusion rules in an effort to guard against a possible systemic risk. State-sponsored cyberattacks will be ruled out from its scope of coverage as of 1 March 2023.
Faced with the shortage of capacity, various solutions have been developed to cover cyber risks. The establishment of entities dedicated solely to cyber risks is one of these initiatives.
Major European companies such as Airbus, Michelin, Veolia, Adeo, Sonepar, BASF and Solvay have chosen to launch a joint insurance company for cyber risks. Called Miris Assurance, the new entity, based in Belgium, is expected to obtain approval from the insurance regulator by 2023.
According to Moody's, the reduction in cyber capacity and the latest adjustment measures introduced by the insurance companies should lead to an improvement in the industry's loss ratio. The latter is poised to fall from 88% in 2021 to 65% in 2022.
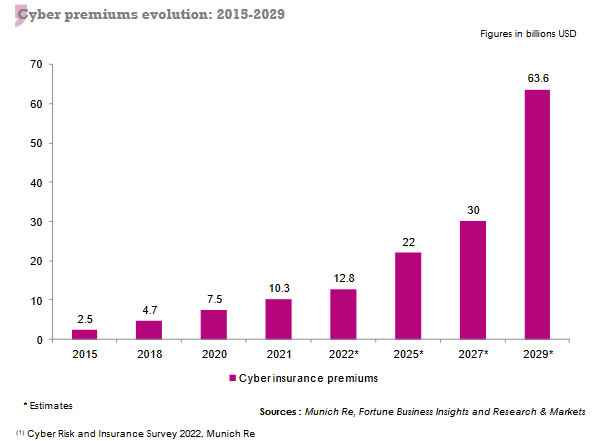
The cyber insurance market in 2022
For the first eight months of 2022, the worldwide cyber insurance premiums amounted to 9.2 billion USD (1). They are likely to reach 12.83 billion USD by the end of 2022, against the 10.33 billion USD posted in 2021. The market plans on reaching a 22 billion USD turnover by 2025 and 63.6 billion USD by 2029.
The increase in premiums is driven by the rise in tariffs and the improvement of the coverage level of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
(1) Cyber Risk and Insurance Survey 2022, Munich Re
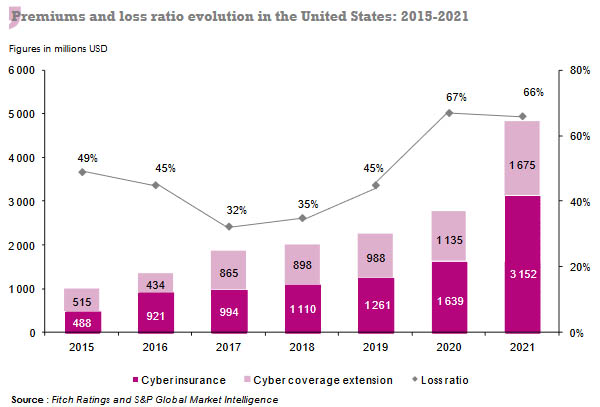
The United States alone accounts for more than half of the 2021 cyber premiums (insurance and coverage extension) that is, 4.83 billion USD, an amount rising by 74% compared to the 2.77 billion USD posted in 2020.
At 3.15 billion USD in 2021, the premiums of cyber insurance alone have increased by 92.3%. These same premiums amounted to 1.64 billion USD one year earlier.
Premiums concerning coverage extensions have progressed, for their part, by 47.6% to reach 1.67 billion USD, compared to the 1.13 billion USD posted in 2020.
Main players of the cyber insurance market
By the end of 2022, more than 220 insurers were underwriting cyber risks worldwide (1), compared with 180 in 2021. The cyber insurance market has recorded premiums amounting to 13.5 billion USD (2) in 2022, against 8.6 billion USD a year earlier, which represents a 56.67% increase.
Market leaders Munich Re, Chubb, Beazley, Fairfax Financial Holdings and AXA account for 4.362 billion USD in cyber premiums, giving them a combined market share of 32.3%. The top 20 insurers account for 70% of the global premium income, against 76.6% in 2021.
Lloyds of London (3), which is not included in the ranking below, remains, along with its syndicates, the leading market specializing in cyber insurance. It accounts for 20% of all global premiums, or 2.7 billion USD in 2022, against 1.72 billion USD in 2021.
(1) « Cyber Insurance Market » study by Insuramore
(2) Excluding captive insurers' cyber premiums, estimated at 500 million USD
(3) The Insuramore study does not include Lloyd's of London, whose syndicates are among the other insurance groups listed in the ranking.
Estimated 2022 cyber premiums for the five main groups (direct gross premiums)
Figures in millions USD| Group | Country | Premiums 2022 | Premiums 2021 | Evolution 2021-2022 | 2022 Shares in % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Munich Re | Germany | 1050 | 735 | 42.86% | 7.79% |
| Chubb | Switzerland | 1000 | 800 | 25.00% | 7.42% |
| Beazley | United Kingdom | 870 | 800 | 8.75% | 6.45% |
| Fairfax Financial Holdings | Canada | 810 | 600 | 35.00% | 6.01% |
| AXA | France | 632.5 | 475 | 33.16% | 4.69% |
| Total | 4 362.5 | 3 410 | 27.93% | 32.35% | |
| Rest of the market | 9122.5 | 5 197 | 75.53% | 67.65% | |
| World total | 13 485 | 8 607 | 56.67% | 100.00% |
Source: Insuramore
