China, second largest economic power in 2017

China has therefore shifted from a predominantly rural economy to an industrial economy and then a service-based one. In the 1980s, it opened up to international trade. In 2001, it joined the World Trade Organization (WTO). This date is a turning point in the country's economic history, with immediate positive results. Between 2000 and 2010, Chinese GDP reported impressive growth rates sometimes exceeding 10%.
This growing prosperity lost momentum with the economic recession that followed the global crisis of 2008. Since 2010, Chinese GDP growth has slowed significantly going from 10.6% in the afore-mentioned year down to 6.2% in 2017. However, this rate remains well above the one reported in all industrialized countries.
Endowed with 12 238 billion USD in 2017, China is the world's second largest economy behind the United States, with gross domestic product worth 19 391 billion USD in 2017. It is also the second largest insurance market in the world. The country accounted for 541.446 billion USD in premiums.
Related article:
China in 2017: Unbridled economic growth
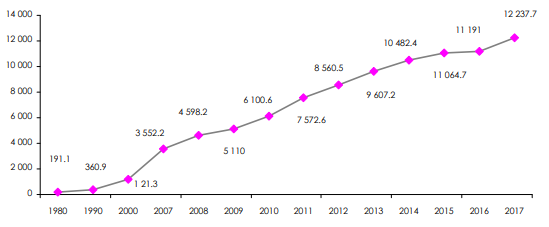
Starting from the 2000s, China began reporting very high growth rates. GDP, set at 1 211 billion USD in 2000, rose to 12 238 billion USD in 2017, accounting for 15% of the global GDP, estimated at 80 684 billion USD in the last afore-mentioned year. For the record, China's GDP accounted for only 3.6% of the global GDP in 2000 and 1.8% in 1979, the year when reforms were launched and China opened up to the world market.
A titre de rappel, le PIB chinois ne représentait que 3,6% du PIB mondial en l’an 2000 et 1,8% en 1979, année de lancement des réformes et de l’ouverture de la Chine au marché mondial.
Evolution of China’s GDP: 1980-2017
Population and development of the middle class
With a population of 1.379 billion inhabitants in 2017, China is the most populous country in the world, accounting for almost one-fifth of the world's population estimated at 7.530 billion people in 2017.
The emergence of a middle class is an important asset to the economy. This social category is poised to account for one third of the Chinese population by 2030, compared to 10% in 2016, which is likely to boost local consumption and increase demand for insurance.
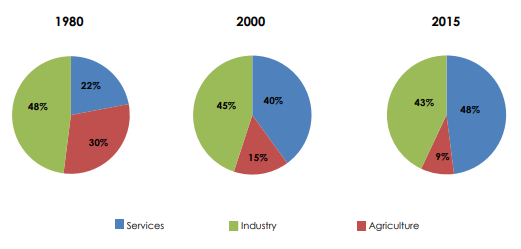
China in 2017: Growth of the tertiary sector
Following the 2008-2010 economic recession, the Chinese government decided to reduce the country's dependence on international trade, promoting investment in the service sector, including insurance. The purpose behind this move is to lessen the weight of the manufacturing sector strained by its overcapacity.
The tertiary sector, which accounted for only 22% of GDP in 1980, rose to 48% in 2015. This activity generated nearly half of the country's wealth during the year. This percentage continues to increase.
Evolution of the tertiary sector’s share in the Chinese economy