Alternative reinsurance: forms, evolution and impact on reinsurers
 Standard licence of Fotolia Standard licence of Fotolia |
The development of this new form of reinsurance requires the presence of a transparent and effective financial market.
The terms and conditions offered by traditional reinsurance in 2016 continue to decrease. The techniques used allow insurers and reinsurers to connect with capital markets. The growth of alternative reinsurance remains stable despite the abundance of traditional capacities and the poor reinsurance rates in use during latest renewals. It accounts for 18% of the current reinsurance offer.
The different forms of alternative reinsurance
The different patterns of alternative reinsurance is a topic that has been widely covered by Atlas Magazine (issue N°117, January 2015). We shall recall here below the key elements of this new technique which are the Cat Bonds, sidecars, Industry Loss Warranty and financial securities-backed reinsurance.
Alternative reinsurance: Cat Bonds
Cat Bonds are debt securities that transfer the risk of a sponsor (an insurer) to an investor (capital markets). The creation of these securities requires the establishment of an intermediary entity (a mutual debt fund), also called “special purpose vehicle (SPV)”. The latter issues a security on behalf of the investor whereby the terms and conditions governing the security are similar to those of a traditional reinsurance contract.
The Special Purpose Vehicle collects the amounts invested which will be used to indemnify the sponsor in case an insured event occurs. If such an event happens, the investor will sustain a loss on its investment.
In the absence of any insured event, the investor may recover the premium paid by the sponsor to the Special Purpose Vehicle as well as the principal.
Depending on the kind of Cat Bond, several factors may come at play to determine the compensation due: a parametric factor or a threshold amount affecting the entire industry.
Alternative reinsurance: the sidecar
The sidecar is a temporary reinsurance vehicle or entity that shares premiums and claims with an insurer on a proportional basis. In general, it is associated with a natural catastrophe risk. The elaboration of a sidecar requires the commitment of several parties. A sponsor (an insurer or reinsurer) sets up a company (the sidecar) for limited purposes and for a temporary period of time.
The sidecar may be financed by means of debts and shares by a third party investor (capital markets). The revenues from debts, shares and premiums ceded by the sponsor are invested in a trust account that is designed to pay the claims in case of their occurrence.
Alternative reinsurance: Industry Loss Warranty (ILW)
Industry Loss Warranty (ILW) is a contract that provides coverage for an insurer in case a claim affecting the entire market occurs. This claim has to fulfill some pre-defined criteria. An aggregate sum for the loss in a given class of business (for instance the cyclone business) is predefined.
The coverage is triggered only if this threshold is exceeded. In general, the insurer must also have sustained damage during the occurrence of a claim in order to benefit from compensation. ILWs are paid only according to some threshold of loss sustained by the entire market in a pre-defined area and for the kind of event that has been previously agreed upon.
For instance, following the passage of hurricane Sandy in the USA in 2012, reinsurers could not benefit from ILWs contracts concluded back then with an activation threshold set at 20 billion USD for this type of event. The final damage toll determined in March 2013 was only 18.75 billion USD.
Alternative reinsurance: Financial security-backed reinsurance
This type of risk takes the shape of a debt security backed to an insured event. This security may be tailor-made as a supplement to a traditional reinsurance contract.
The amounts generated from the securities combined are equal to the reinsurance coverage limit net of premiums. The securities are detained in a separate account designed to cover the claims sustained by the insurer. The reinsurance premium stands as the interest received by the investors.
The advantages of reinsurance alternative solutions, they:
- stand as an element of diversification of reinsurance covers,
- make it possible to benefit from costs of predictable covers,
- provide protection at reduced costs,
- provide access to an additional capital (financial market),
- make it possible, in some cases, to diminish credit risk as they are backed by a financial security.
The evolution of alternative reinsurance
The popularity of alternative reinsurance is gaining momentum. It has continued, since 2007, to trigger continuous capital inflows that are proliferating thanks to hedge and pension funds. This growth has, nonetheless, slightly slowed down, especially in case of financial security-backed reinsurance. The tariffs of Insurance Linked Securities are lagging behind. The performance of cat bonds has decreased since 2012, it nevertheless remains interesting for investors.
By the first quarter of 2015, the global market reported 66 billion USD in alternative capital, a figure on a 3% rise in comparison with that reported by December 31, 2014. Cat Bonds have sustained a slight decrease at 22.1 billion USD while sidecars grew by 1 billion USD at 7.6 billion USD. Financial security-backed reinsurance has, for its part, maintained its upward trend of approximately 10% at 32.7 billion USD.
Even though alternative reinsurance is particularly designed for non life insurers, it is also interesting for life insurers that make recourse to it. The crisis has, nevertheless, strained some stakeholders acting as counterpart. Ever since, life insurance companies have reduced their recourse to those reinsurance techniques.
Evolution of alternative reinsurance worldwide in billions USD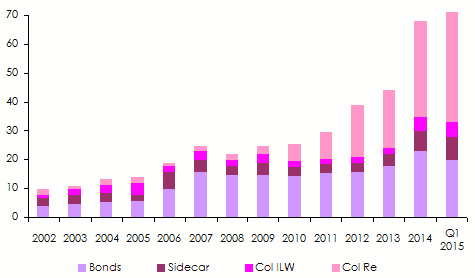 Source: Aon Securities
Source: Aon SecuritiesAccording to Guy Carpenter, alternative capital accounts for 18% of the entire capital available in reinsurance. The main markets making recourse to those coverage methods are: the United States, Europe and Japan
Evolution of alternative capitals’ share in billions USD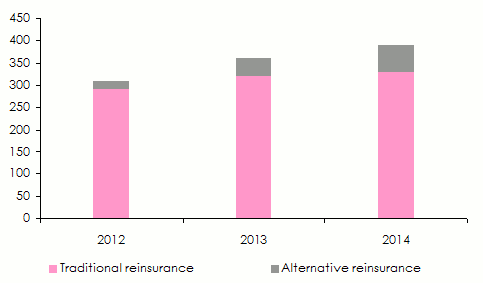 Sources: A.M. Best and Guy Carpenter
Sources: A.M. Best and Guy CarpenterReinsurers facing new alternative reinsurance covers
Hannover Re, Swiss Re and Munich Re have been among the first major players to make extensive use of those new forms of reinsurance. Depending on each case, they have acted as fronting or by transforming themselves the risk. For the upcoming years, other reinsurers will be bound to use these mechanisms of risk transfer.
According to Michel Lies, Swiss Re’s CEO, the number of insurance companies that asked Swiss Re for advice on this kind of products during the recent four years rose from 50 global insurers to 1500 regional and local insurers. This trend clearly shows the growing interest of insurers in alternative reinsurance.
The new patterns of alternative reinsurance
Effective structures such as sidecars and ILS have prompted the development of new patterns of short-term investments ranging from 1 to 3 years. A large majority of the alternative drained capital has been invested as temporary sidecars or ILS that allow rapid entry and exit of the reinsurance market.
Recent developments have provided insurers and investors with the opportunity to transfer risks directly on capital markets without even having to go through reinsurers. This trend has been behind this new kind of alternative capital with backed reinsurance or rating-free sidecar, along with other more flexible kinds of ILS.
These recent developments are also behind the establishment of Hedge Fund Re, a company whose activities consist in optimizing investment interests by building and managing a long-term capital portfolio.