IT security
 Computer resources are not only exposed to classical operating risks such as fire, breakdowns or water damage, but also of new types of risks such as cyber attacks, computer viruses and theft of confidential data. These risks of extreme technological complexity have urged insurers to face a challenge: responding to immaterial large-scale threats in a profoundly-changing industry.
Computer resources are not only exposed to classical operating risks such as fire, breakdowns or water damage, but also of new types of risks such as cyber attacks, computer viruses and theft of confidential data. These risks of extreme technological complexity have urged insurers to face a challenge: responding to immaterial large-scale threats in a profoundly-changing industry.
The position of information technology in society
IT has taken a prominent place in modern economy with internet and information networks having become essential working tools. Yet access to these technologies is not devoid of dangers. The risks associated with the use of computers or other data exchange processes threaten the proper functioning of companies.
Computers present certain hazards such as:
- operating loss due to damage causing partial or total shutdown of the activity. The causes of such a loss can be various: handling error, malicious act, etc. Additional costs, for example, decontamination, data retrieval, or gear replacement can be added to the material damages.
- third party liability risk consecutive to the spread of viruses, theft of data entrusted by third parties (data of customers, providers, subcontractors, employees, etc).
- damage to the image. Loss of internal data or paralysis of the computer systems can be detrimental to the image of a company. The financial impact of such an event can be enormous.
Companies’ attitude toward risks
Being aware of the threat and identifying risks becomes important. Companies adopt in general a set of preventive measures including the management and transfer of risks which rank high. Recourse to insurance is the ultimate safety net for companies.
Moreover, in many countries, the authorities themselves rely on the solutions offered by insurance to protect individuals and companies. A multitude of third party liability obligations weigh on companies for the damages caused to third parties by their acts, their negligence or imprudence. They are, therefore, required to take all necessary precautions to preserve data security and prevent unauthorized third party from having access to them.
Risk awareness
Hazards that companies face are of two kinds: financial risks and operational risks. In the latter category, computer-based naturally claims top the list of managers’ concerns. Risk management has gradually grown into a major activity of the company along with production and sales.
IT-related risks evolve at the same pace as technology itself, with their identification, measurement, analysis and management requiring specific knowledge and skills. The company has to take into account all of these variables to set up preventive measures and risk transfer to insurance.
Risk identification
Different studies have allowed to target the company’s sectors most exposed to information risks. Levels of risk perception vary according to the activity.
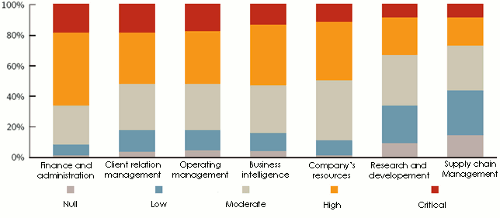 Source: «IT risk management report», Symantec
Source: «IT risk management report», Symantec Within the same company, there exists a disparity of risk perception by employees of different departments. With nearly 70% of employees who feel well informed, staff attached to finance and administration are the best prepared to risks.
To mitigate perception disparities, companies have adopted prevention measures involving all employees. A company out of two has established a security policy based on the improvement of organizational procedures.
These awareness campaigns are often based on the publication of a user charter relayed by instruction reminders on intranet sites. This strategy implies a voluntary search of information by employees. Most efficient prevention policies rely on timely training and distribution of information booklets.
Where such procedures exist, prevention initiatives target in 75% of the cases all employees. Targets of awareness campaigns include the company’s external collaborators and customers.
Employees targeted by awareness campaigns
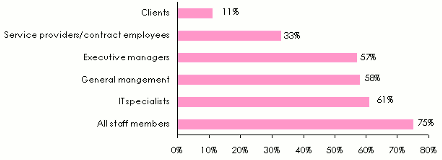 Source: A survey entilled : «the management of IT security», carried out by the Association Française de l’Audit et du Conseil Informatiques. (a survey based on a multiple choice questionnaire)
Source: A survey entilled : «the management of IT security», carried out by the Association Française de l’Audit et du Conseil Informatiques. (a survey based on a multiple choice questionnaire) The budget allocated to information security
 While insurance costs are easily identifiable, being reported in the company’s books, the security budget is, in turn, harder to estimate. It includes shared expenses between technical costs (softwares, infrastructure, services, etc) and operating expenses (projects, etc).
While insurance costs are easily identifiable, being reported in the company’s books, the security budget is, in turn, harder to estimate. It includes shared expenses between technical costs (softwares, infrastructure, services, etc) and operating expenses (projects, etc).
Sharply rising, these costs account for the progression of the threats that strain the company. For the management of the companies, information security is a guarantee of quality or even a competitive advantage.
The number of large companies endowed with a budget allocated to computer security is estimated at 35%. As shown below, the purchase of security software accounts for 67% of the budget assigned to companies’ protection and prevention. The amounts allocated to insurance account for just 10% of the security budget.
Breakdown of companies’ IT security budget
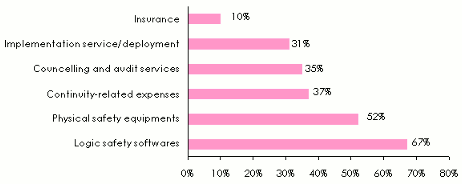 Source: A survey entilled : «the management of IT security», carried out by the Association Française de l’Audit et du Conseil Informatiques. (a survey based on a multiple choice questionnaire)
Source: A survey entilled : «the management of IT security», carried out by the Association Française de l’Audit et du Conseil Informatiques. (a survey based on a multiple choice questionnaire) The outsourcing of IT security
The IT security of large companies is usually ensured by in-house teams. For smaller entities, outsourcing stands as an interesting alternative, providing many advantages such as cost reduction, around the clock (24h/24h) service, greater responsiveness than that provided by in-house teams. In addition, outsourcing provides skills that many medium-sized companies cannot afford even at reasonable costs. However, this solution is not flawless. The chart below lists the main constraints faced by companies when outsourcing their security. The loss of control is the first obstacle to this type of operation, followed by the loss of confidentiality, the introduction of new risks, ...
Solutions offered by insurance
Insurance stands as the last resort of companies in case of failure of in-house protection and prevention procedures.
Guarantees covering the risks pertaining to information systems can be underwritten with:
- insurers’ distribution networks
- hardware vendors that offer, in addition to the standard cover, an additional insurance coverage which is usually facultative.
- banks that finance gear acquisition often through leasing.
- some insurers who sell their contracts via internet.
Standard contracts are usually displayed in the form of a comprehensive package that covers the insured against failure, gear theft, electrical damage, fire, water damage, ...
Contraints due to the outsourcing of IT security
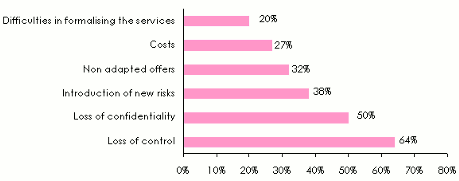 Source: A survey entilled : «the management of IT safety», carried out by the Association Française de l’Audit et du Conseil Informatiques. (a survey based on a multiple choice questionnaire)
Source: A survey entilled : «the management of IT safety», carried out by the Association Française de l’Audit et du Conseil Informatiques. (a survey based on a multiple choice questionnaire) Specific covers
 © M0NGoLiAN.0NesT, CC BY-SA 3.0 © M0NGoLiAN.0NesT, CC BY-SA 3.0 |
The marketing of specific covers is recent, with guarantees evolving in response to new threats detected: hacker attacks, viruses, fishing, etc. In these contracts, the range of risks covered, premium rates and amounts of capital are related to the quality of prevention implemented by the insured.
Specific guarantees are particularly relevant to areas where the management of personal or business data rank high. Financial institutions, e-commerce, transportation, distribution companies and those in the hospital sector are particularly comprised in this type of guarantee.
Guarantees generally offered include:
- theft, substitution and transformation of:
- bank details
- credit card numbers
- identity-related data
- medical data
- business secrets, etc
- breaches of contract pertain to damages resulting from failures to:
- operation
- performance
- total or partial breach of obligations under a contract
- breach of duty: errors, omissions, negligence, ...
- the willful misconduct or fraudulent acts
- disclosure of confidential information
- invasion of privacy: infringement of the right to the name, image, voice, privacy, honor, ...
- defamation
- unfair competition due to parasitis m, fraudulent practices
- infringement of copyright
- defective products
- loss or total or partial destruction of documents, material aids for data or entrusted property
- viruses
- data recovery costs
- additional operating costs
Insurance prices
 |
IT risks tariffs remain high. The market being new, there is no statistical series documented enough to allow a subtle actuarial approach. Current premiums rates often exceed 5% of the sums insured.
To determine a tariff in the absence of historical data, insurers rely on:
- the turnover of the insured
- the industry
- the type of activity
- the security audit of information systems
- the loss experience of the insured
Coverage limits vary depending on the size of the insured. They may amount to hundreds of millions of dollars for large international groups.
The most famous cyber attack was carried out against Sony Group and its Playstation Network. More than 80 million customer data were stolen. The Japanese firm has spent nearly 173 million USD to meet operating losses: updating of all systems, third party claims, payments of damages to customers and other costs.
In general, the loss of a cyber attack is difficult to assess. In addition to material losses, immaterial damage including loss of image and reputation must be considered. Factors such as the host country of the insured, the industry, and the regulatory framework will also impact the amount of damages.
According to a study conducted by SNIA France, dating back to 2008, 90% of French companies having suffered a loss of data as a result of cyber-attack usually disappear within two years, having had no coverage. Insurance is therefore essential for the survival of companies whose dependence on information technology is important.