The risk of supply chain disruption
The disruption risks affecting supply chains
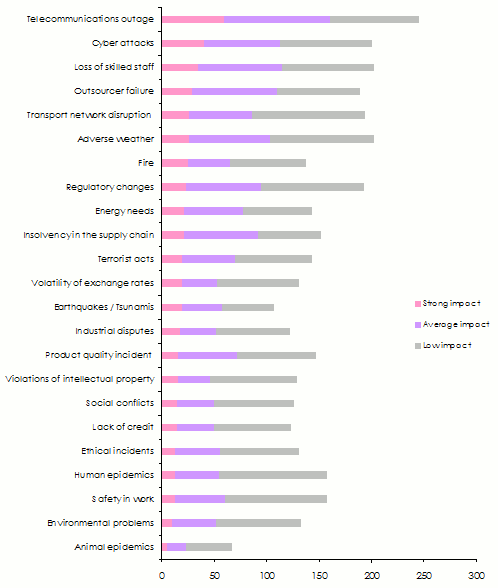
The most common disruption risks affecting supply chains stem from failure in telecommunication systems, followed by cyber-attacks, subcontractors' lack of skilled labor, subcontractors’ failures and the disruption of transportation networks.
Adverse weather conditions rank sixth, thus underscoring climate change-related threats. Fire risk jumped from fourteenth position held in the 2016 edition to the seventh place in 2017.
Change in regulations, energy needs and insolvency complete the top ten of the survey.
Source of the disruption of supply chains
The origins of the supply chain disruption are numerous, according to BCI’s statistics:
- For 44% of the organizations quizzed, first-tier suppliers have stood as the first source of the disruption.
- 24% of the companies have singled out second rank suppliers.
- 10% have declared that their trouble comes from lower rank suppliers.
- 22% of the companies have failed to identify the source of disruption.
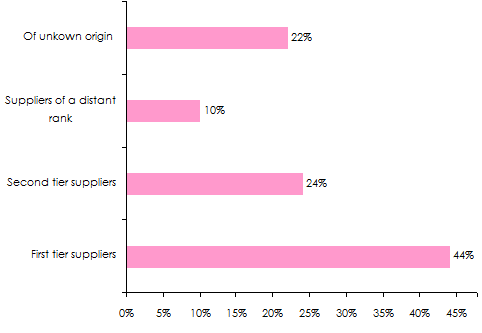
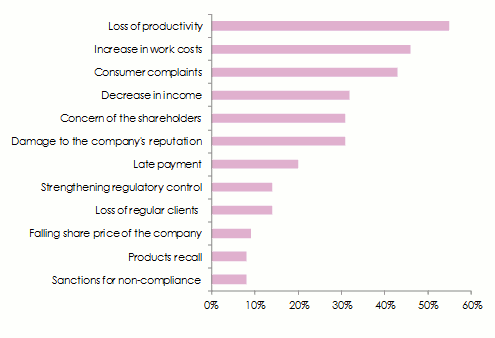
Causes behind the disruption of supply chains
As is the case for the sources of disturbance, the causes behind the disruption of supply chains are also multiple not to say innumerable. Analyzed in terms of frequency and severity, the most important causes are as follows:
Cyber risks
According to Cybersecurity Ventures, an American research company, the losses caused by cyber criminality exceeded 5 billion USD in 2016, a figure poised to pursue its upward trend at a frightening pace to reach 6 000 billion by the end of 2021.
This exponential increase in losses is likely to trigger awareness about the scale of the threat. Several countries like the United Kingdom have already outlined a set of standards and good practices with which each stakeholder involved in a supply chain is required to comply. This initiative will make it possible for major companies to ensure the resilience of their suppliers to any cyberattack.
Some companies require from their potential suppliers and subcontractors a detailed survey on their cyber-security status prior to signing their contract.
The suppliers’ financial situation
The financial situation of suppliers is another risk factor. Corporate insolvency may result in delivery delays, bad product quality, or even a shortage in raw material.
It is difficult for companies to detect this kind of risk with their subcontractors who are not required to publish their financial statements (private and non-listed companies).
Trouble within companies
Labor is the backbone of the supply chain. A strike within a factory is likely to result in heavy consequences. Trade union movements, safety at the workplace, workforce quality, and failures of quality control stand as the main labor risks within companies.
The fiasco sustained by Samsung’s Galaxy Note 7 Smartphone, whose batteries turned out to be faulty, has been accounted for by failure at the level of technical control and by labor issues.
Political risk
Political turmoil, both local and international, directly impact supply chains.
The year 2016 was exceptionally disastrous for supply chains globally. On June 23th 2016, the United Kingdom decided to pull out from the European Union (Brexit), thus triggering a climate of economic, financial and geopolitical uncertainty.
This protectionist move has been aggravated by the election of Trump in the United States in November 2016. This in-ward-looking attitude on part of some States has impacted global organization of labor, with accrued vulnerability of supply chains overarching all other considerations.
For many experts, the 2016 political events are only a brief taste of the hardships that companies will be up against in the near future.
Natural catastrophes
Very few countries are safe from natural disasters whose frequency and intensity are steadily gathering momentum. The dysfunctions triggered by major weather events seem to be hard to forecast. The year 2017 has been deemed extremely negative in this area: devastating cyclonic season in the United States, earthquakes in Mexico, floods in Asia…
In the United States, the Federal Emergency Management Agency (FEMA) has estimated that 40% of the companies affected by large-scale natural disasters are definitively being driven out of business. Of those keen on restarting business, only 29% have become operational two years following the occurrence of injurious events.
Consequences of supply chain disruption
The interruption of supply chain is of heavy consequences:
- 55% of the companies polled have reported productivity losses following this incident.
- 46% have sustained an increase in labor costs due, among others, to the search for new suppliers.
- 43% have received complaints from consumers.
Declining revenues have been reported among 32% of the polled companies.
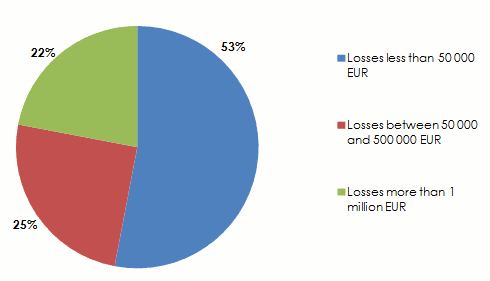
To note that 22% of the companies hit by a disruption of the supply chain sustain losses higher than 1 million EUR (1,2 million USD), 5% of which suffering from damages costing over 100 million EUR (120 million USD).
 |